Bayesian Supervised Learning in StochTree
BayesianSupervisedLearning.RmdThis vignette demonstrates how to use the bart()
function for Bayesian supervised learning (Chipman, George, and McCulloch (2010)). To
begin, we load the stochtree package.
Demo 1: Step Function
Simulation
Here, we generate data from a simple step function.
# Generate the data
n <- 500
p_x <- 10
snr <- 3
X <- matrix(runif(n*p_x), ncol = p_x)
f_XW <- (
((0 <= X[,1]) & (0.25 > X[,1])) * (-7.5) +
((0.25 <= X[,1]) & (0.5 > X[,1])) * (-2.5) +
((0.5 <= X[,1]) & (0.75 > X[,1])) * (2.5) +
((0.75 <= X[,1]) & (1 > X[,1])) * (7.5)
)
noise_sd <- sd(f_XW) / snr
y <- f_XW + rnorm(n, 0, 1)*noise_sd
# Split data into test and train sets
test_set_pct <- 0.2
n_test <- round(test_set_pct*n)
n_train <- n - n_test
test_inds <- sort(sample(1:n, n_test, replace = FALSE))
train_inds <- (1:n)[!((1:n) %in% test_inds)]
X_test <- as.data.frame(X[test_inds,])
X_train <- as.data.frame(X[train_inds,])
W_test <- NULL
W_train <- NULL
y_test <- y[test_inds]
y_train <- y[train_inds]Sampling and Analysis
Warmstart
We first sample from an ensemble model of
using “warm-start” initialization samples (He and
Hahn (2023)). This is the default in stochtree.
num_gfr <- 10
num_burnin <- 0
num_mcmc <- 100
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
bart_params <- list(sample_sigma_global = T, sample_sigma_leaf = T, num_trees_mean = 100)
bart_model_warmstart <- stochtree::bart(
X_train = X_train, y_train = y_train, X_test = X_test,
num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
params = bart_params
)Inspect the MCMC samples
plot(bart_model_warmstart$sigma2_global_samples, ylab="sigma^2")
abline(h=noise_sd^2,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)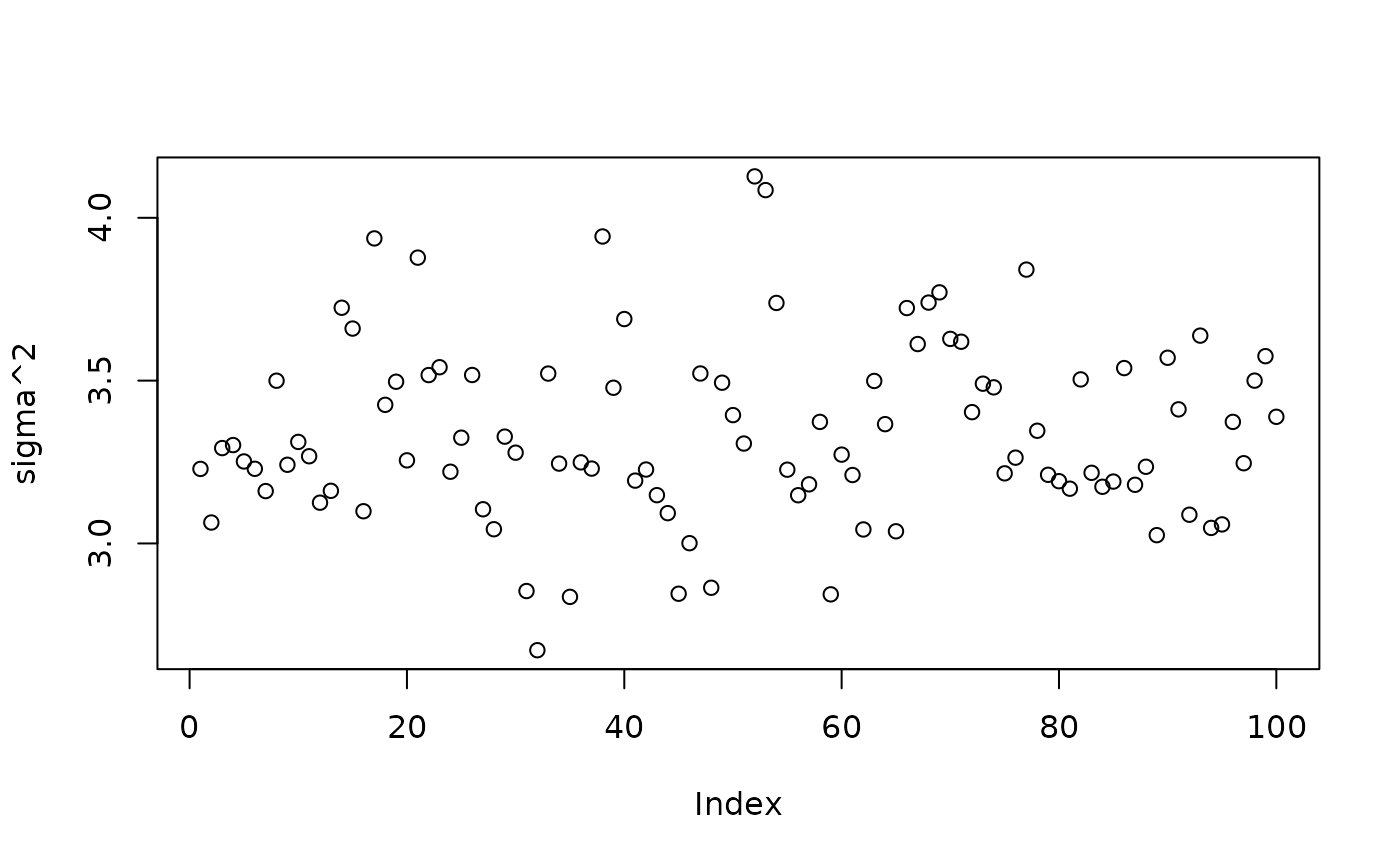
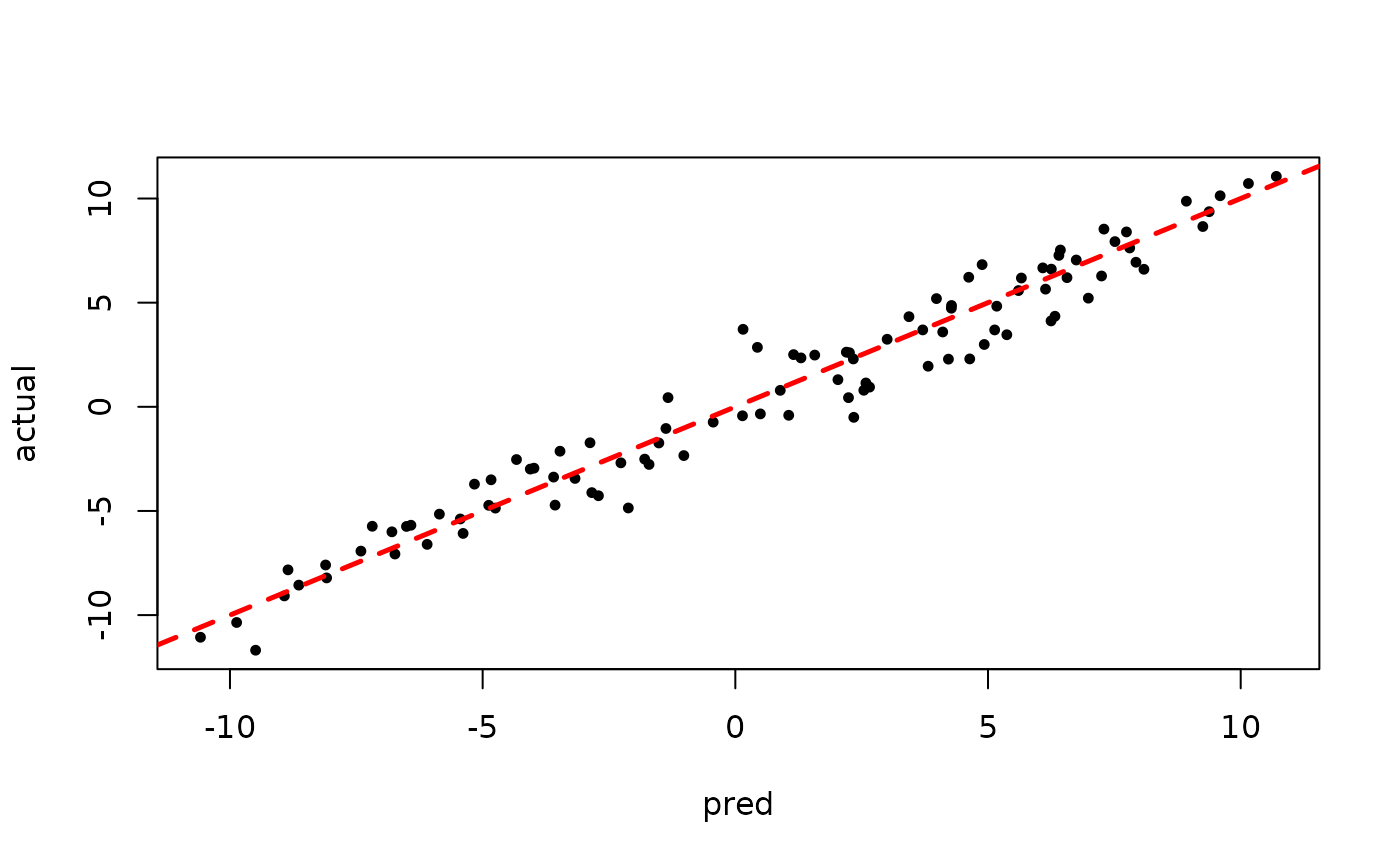
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_warmstart$y_hat_test), y_test,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)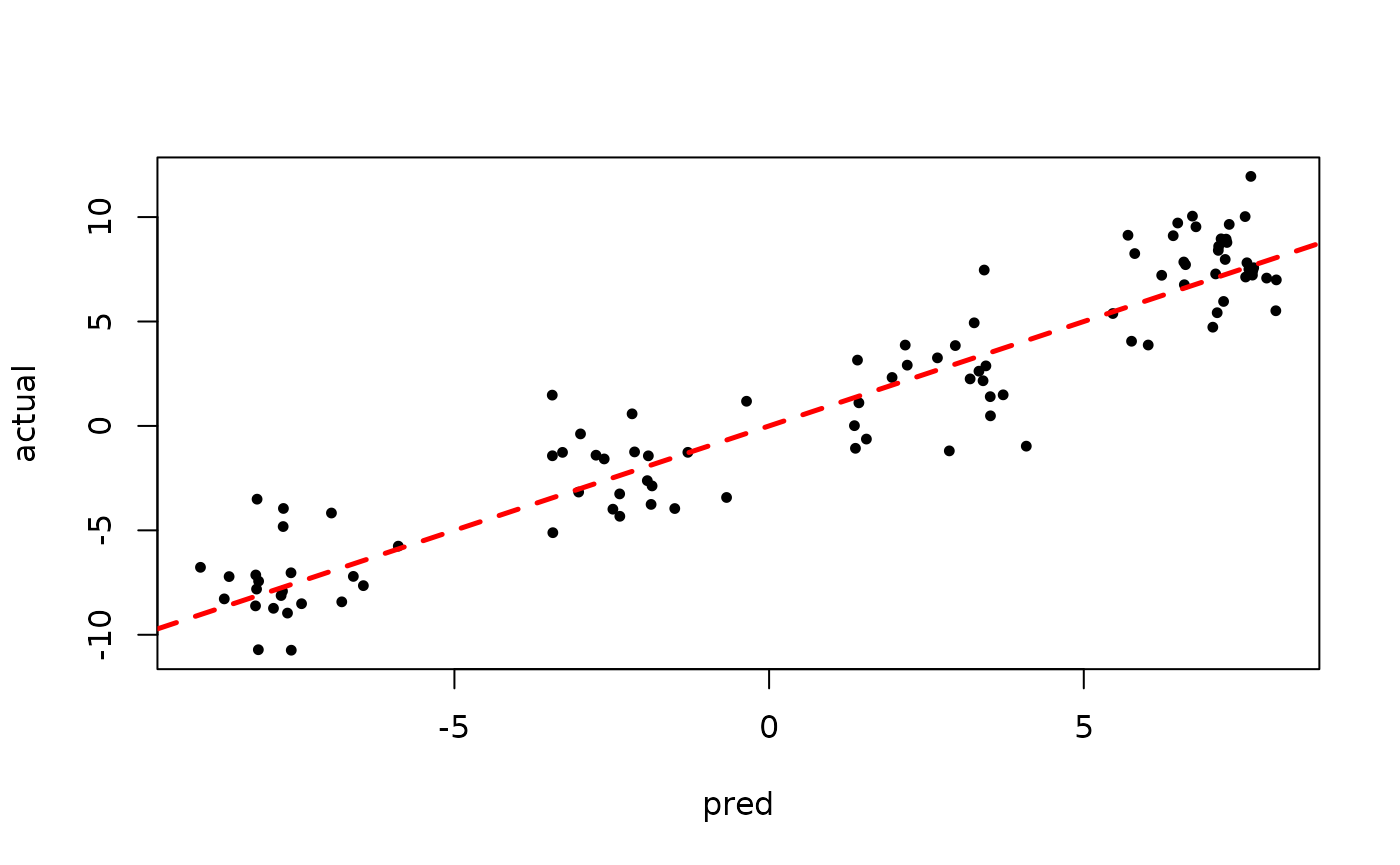
BART MCMC without Warmstart
Next, we sample from this ensemble model without any warm-start initialization.
num_gfr <- 0
num_burnin <- 100
num_mcmc <- 100
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
bart_params <- list(sample_sigma_global = T, sample_sigma_leaf = T, num_trees_mean = 100)
bart_model_root <- stochtree::bart(
X_train = X_train, y_train = y_train, X_test = X_test,
num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
params = bart_params
)Inspect the MCMC samples
plot(bart_model_root$sigma2_global_samples, ylab="sigma^2")
abline(h=noise_sd^2,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)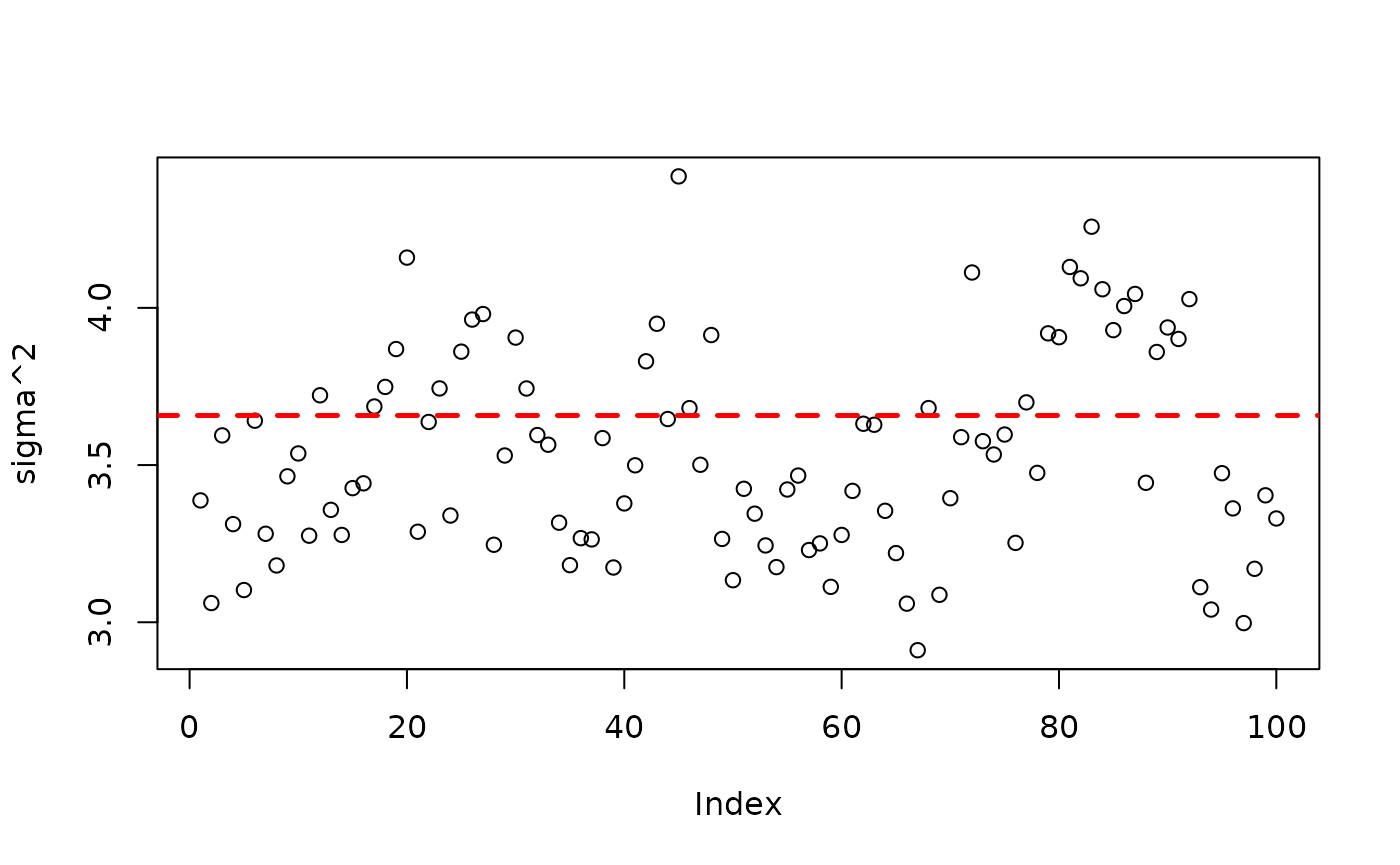
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_root$y_hat_test), y_test,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)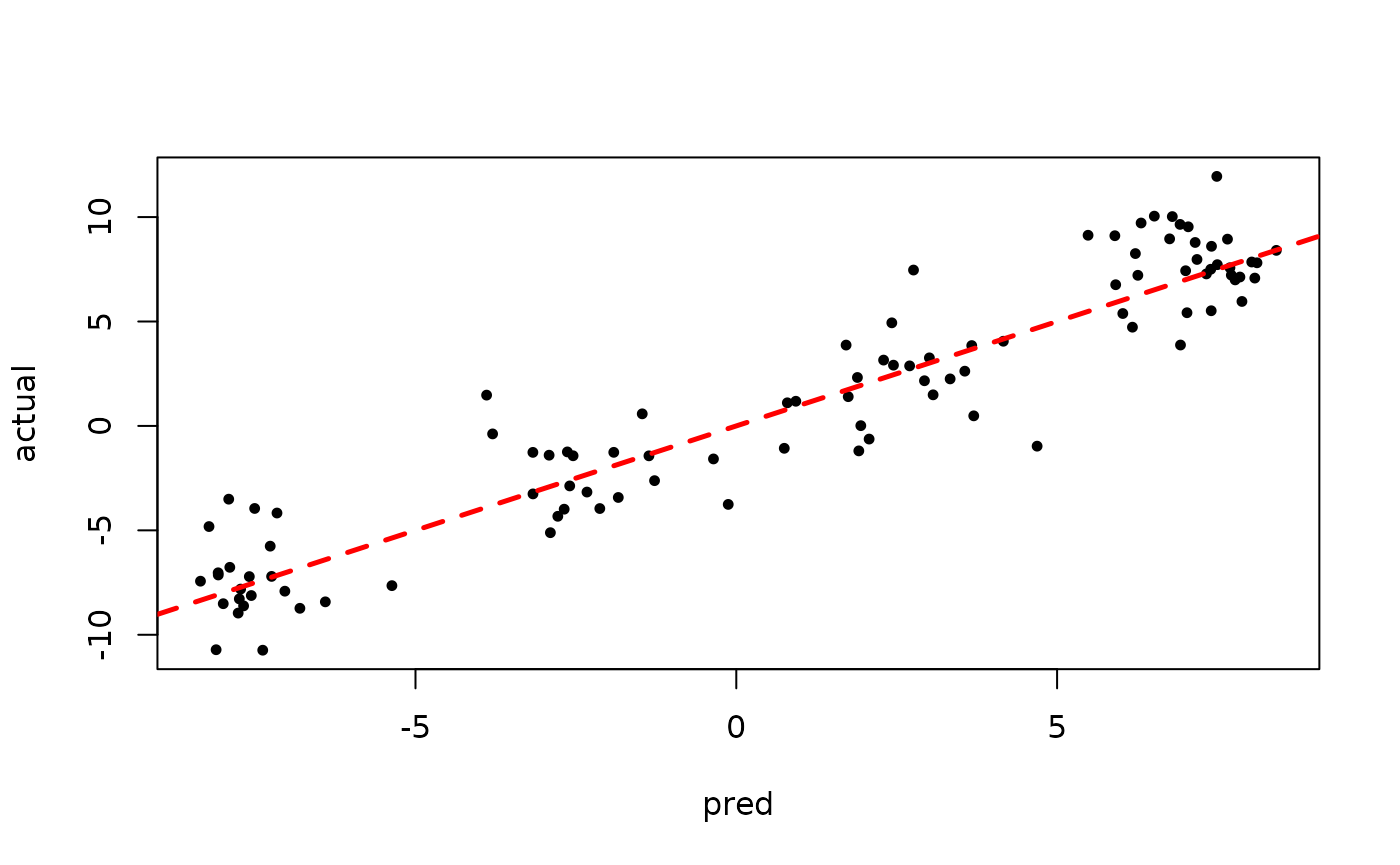
Demo 2: Partitioned Linear Model
Simulation
Here, we generate data from a simple partitioned linear model.
# Generate the data
n <- 500
p_x <- 10
p_w <- 1
snr <- 3
X <- matrix(runif(n*p_x), ncol = p_x)
W <- matrix(runif(n*p_w), ncol = p_w)
f_XW <- (
((0 <= X[,1]) & (0.25 > X[,1])) * (-7.5*W[,1]) +
((0.25 <= X[,1]) & (0.5 > X[,1])) * (-2.5*W[,1]) +
((0.5 <= X[,1]) & (0.75 > X[,1])) * (2.5*W[,1]) +
((0.75 <= X[,1]) & (1 > X[,1])) * (7.5*W[,1])
)
noise_sd <- sd(f_XW) / snr
y <- f_XW + rnorm(n, 0, 1)*noise_sd
# Split data into test and train sets
test_set_pct <- 0.2
n_test <- round(test_set_pct*n)
n_train <- n - n_test
test_inds <- sort(sample(1:n, n_test, replace = FALSE))
train_inds <- (1:n)[!((1:n) %in% test_inds)]
X_test <- as.data.frame(X[test_inds,])
X_train <- as.data.frame(X[train_inds,])
W_test <- W[test_inds,]
W_train <- W[train_inds,]
y_test <- y[test_inds]
y_train <- y[train_inds]Sampling and Analysis
Warmstart
We first sample from an ensemble model of
using “warm-start” initialization samples (He and
Hahn (2023)). This is the default in stochtree.
num_gfr <- 10
num_burnin <- 0
num_mcmc <- 100
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
bart_params <- list(sample_sigma_global = T, sample_sigma_leaf = T, num_trees_mean = 100)
bart_model_warmstart <- stochtree::bart(
X_train = X_train, W_train = W_train, y_train = y_train, X_test = X_test, W_test = W_test,
num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
params = bart_params
)Inspect the MCMC samples
plot(bart_model_warmstart$sigma2_global_samples, ylab="sigma^2")
abline(h=noise_sd^2,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)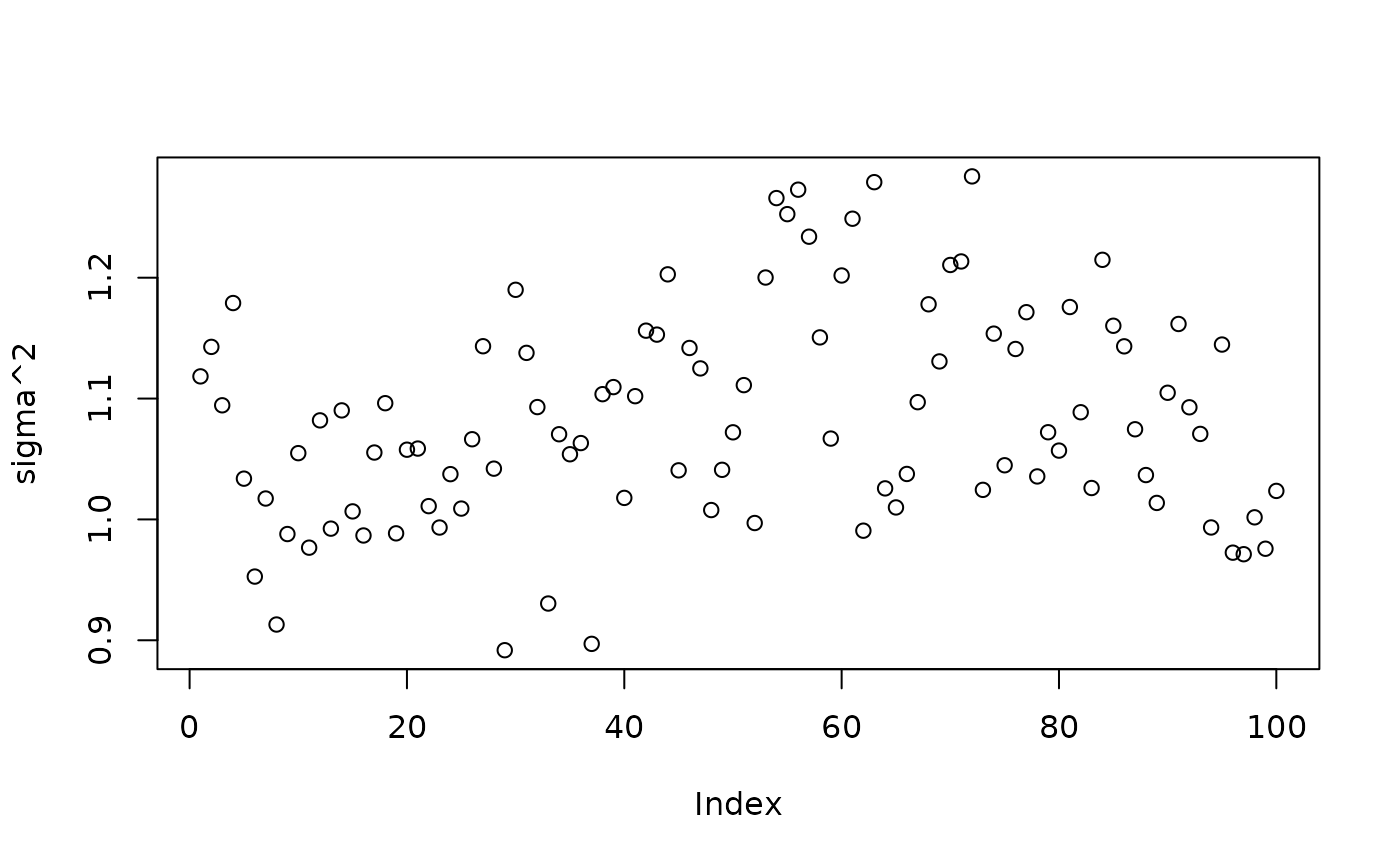
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_warmstart$y_hat_test), y_test,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)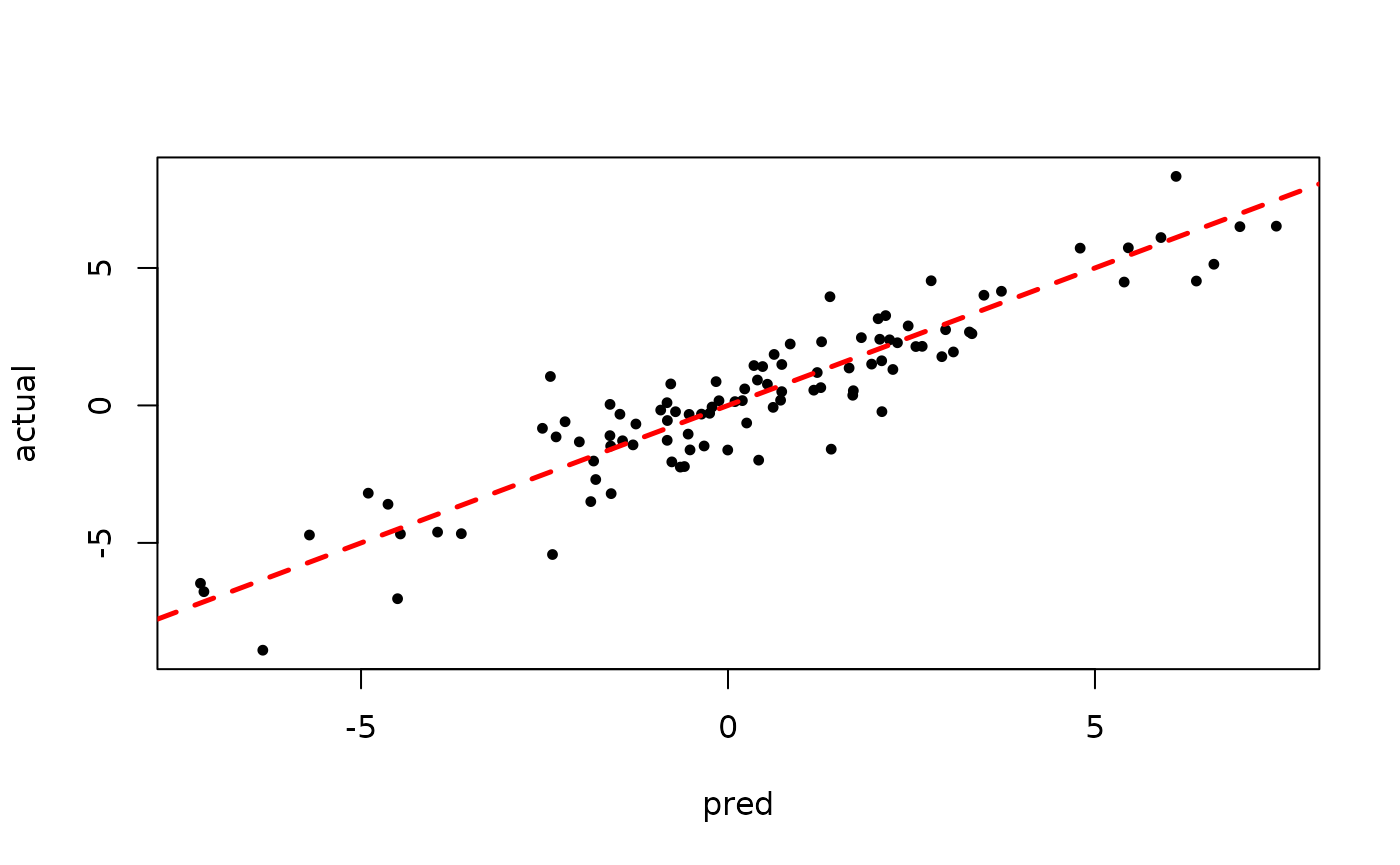
BART MCMC without Warmstart
Next, we sample from this ensemble model without any warm-start initialization.
num_gfr <- 0
num_burnin <- 100
num_mcmc <- 100
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
bart_params <- list(sample_sigma_global = T, sample_sigma_leaf = T, num_trees_mean = 100)
bart_model_root <- stochtree::bart(
X_train = X_train, W_train = W_train, y_train = y_train, X_test = X_test, W_test = W_test,
num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
params = bart_params
)Inspect the BART samples after burnin.
plot(bart_model_root$sigma2_global_samples, ylab="sigma^2")
abline(h=noise_sd^2,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)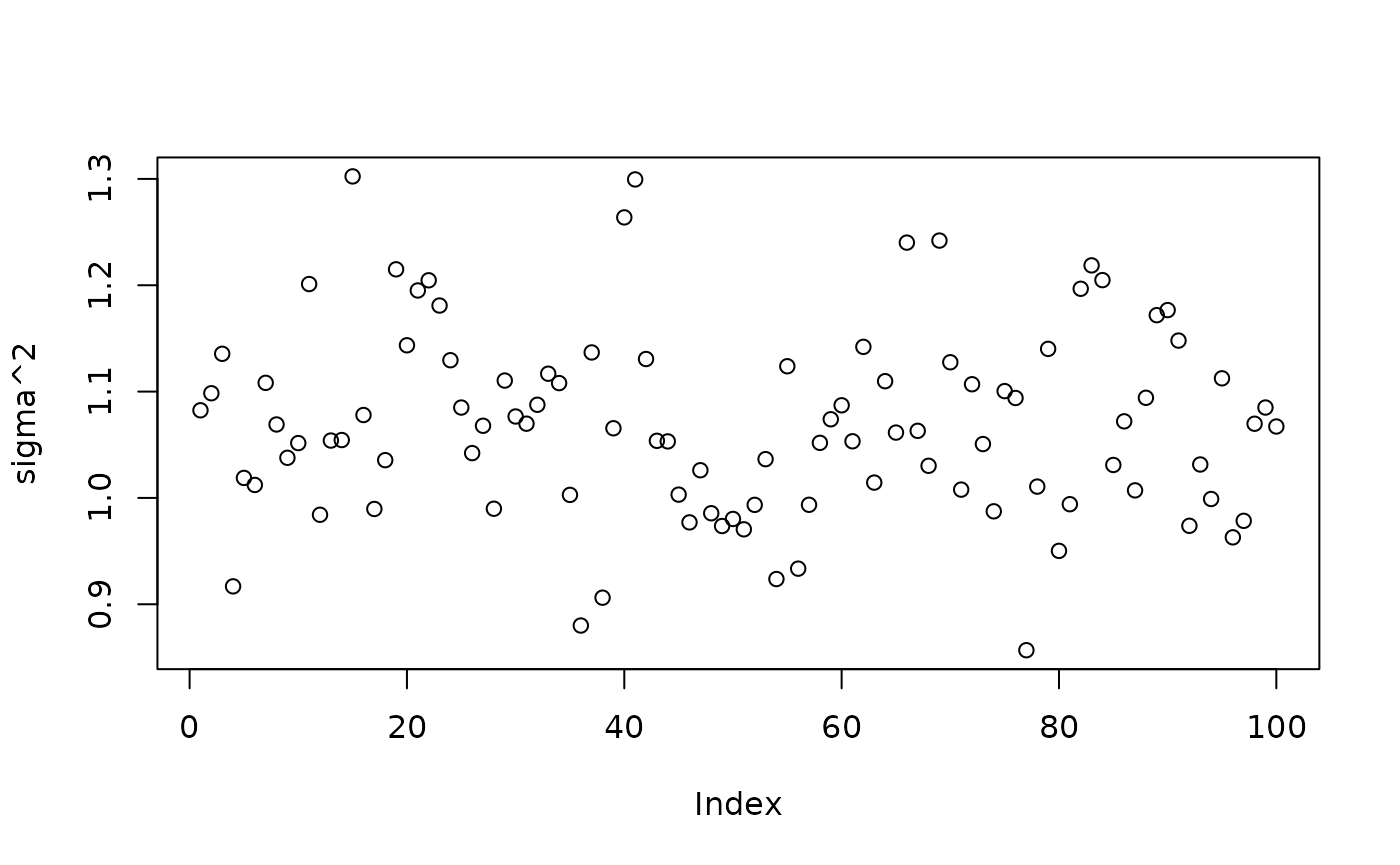
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_root$y_hat_test), y_test,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)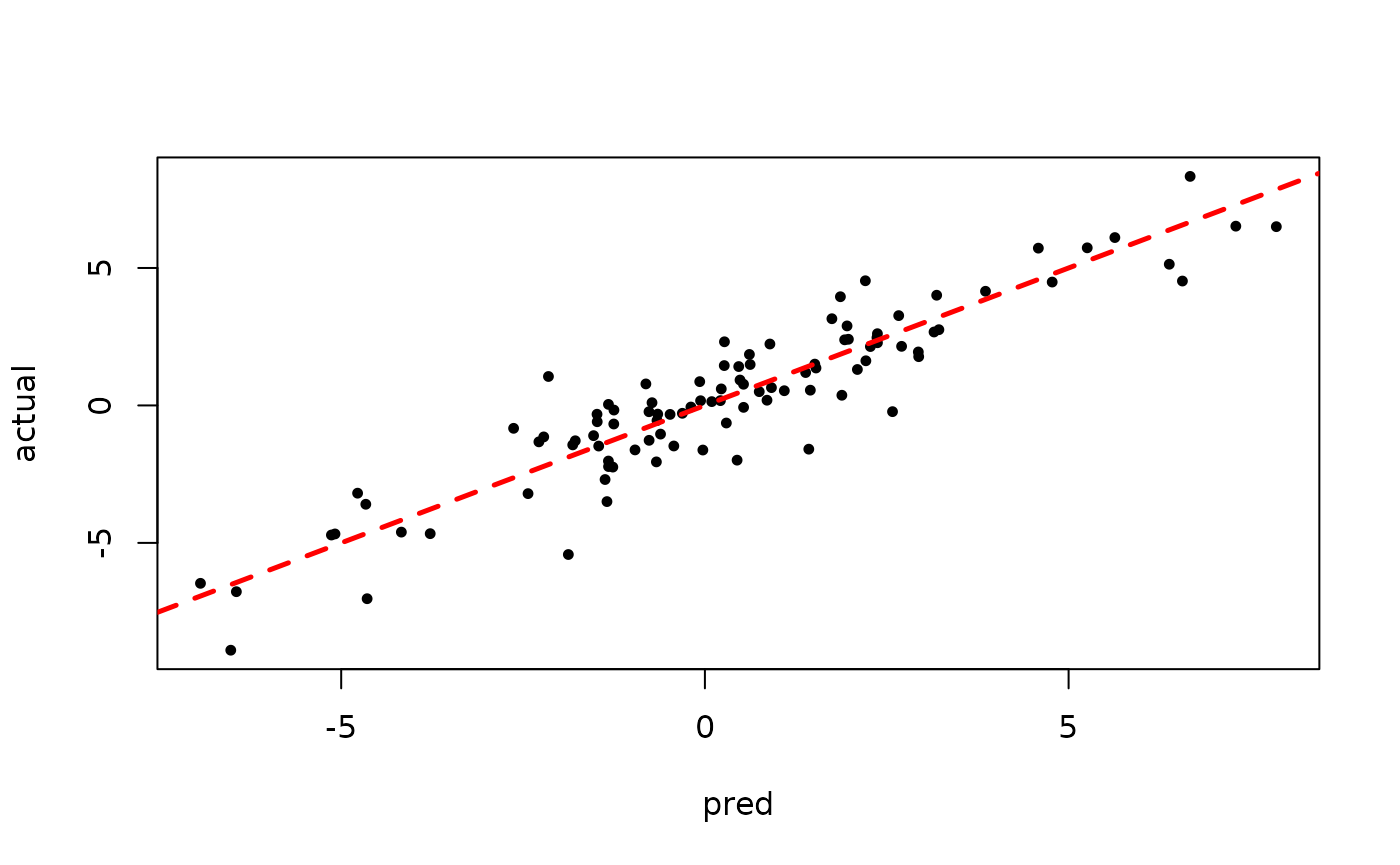
Demo 3: Partitioned Linear Model with Random Effects
Simulation
Here, we generate data from a simple partitioned linear model with an additive random effect structure.
# Generate the data
n <- 500
p_x <- 10
p_w <- 1
snr <- 3
X <- matrix(runif(n*p_x), ncol = p_x)
W <- matrix(runif(n*p_w), ncol = p_w)
group_ids <- rep(c(1,2), n %/% 2)
rfx_coefs <- matrix(c(-5, -3, 5, 3), nrow=2, byrow=TRUE)
rfx_basis <- cbind(1, runif(n, -1, 1))
f_XW <- (
((0 <= X[,1]) & (0.25 > X[,1])) * (-7.5*W[,1]) +
((0.25 <= X[,1]) & (0.5 > X[,1])) * (-2.5*W[,1]) +
((0.5 <= X[,1]) & (0.75 > X[,1])) * (2.5*W[,1]) +
((0.75 <= X[,1]) & (1 > X[,1])) * (7.5*W[,1])
)
rfx_term <- rowSums(rfx_coefs[group_ids,] * rfx_basis)
noise_sd <- sd(f_XW) / snr
y <- f_XW + rfx_term + rnorm(n, 0, 1)*noise_sd
# Split data into test and train sets
test_set_pct <- 0.2
n_test <- round(test_set_pct*n)
n_train <- n - n_test
test_inds <- sort(sample(1:n, n_test, replace = FALSE))
train_inds <- (1:n)[!((1:n) %in% test_inds)]
X_test <- as.data.frame(X[test_inds,])
X_train <- as.data.frame(X[train_inds,])
W_test <- W[test_inds,]
W_train <- W[train_inds,]
y_test <- y[test_inds]
y_train <- y[train_inds]
group_ids_test <- group_ids[test_inds]
group_ids_train <- group_ids[train_inds]
rfx_basis_test <- rfx_basis[test_inds,]
rfx_basis_train <- rfx_basis[train_inds,]Sampling and Analysis
Warmstart
We first sample from an ensemble model of
using “warm-start” initialization samples (He and
Hahn (2023)). This is the default in stochtree.
num_gfr <- 10
num_burnin <- 0
num_mcmc <- 100
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
bart_params <- list(sample_sigma_global = T, sample_sigma_leaf = T, num_trees_mean = 100)
bart_model_warmstart <- stochtree::bart(
X_train = X_train, W_train = W_train, y_train = y_train, group_ids_train = group_ids_train,
rfx_basis_train = rfx_basis_train, X_test = X_test, W_test = W_test, group_ids_test = group_ids_test,
rfx_basis_test = rfx_basis_test, num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
params = bart_params
)Inspect the MCMC samples
plot(bart_model_warmstart$sigma2_global_samples, ylab="sigma^2")
abline(h=noise_sd^2,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)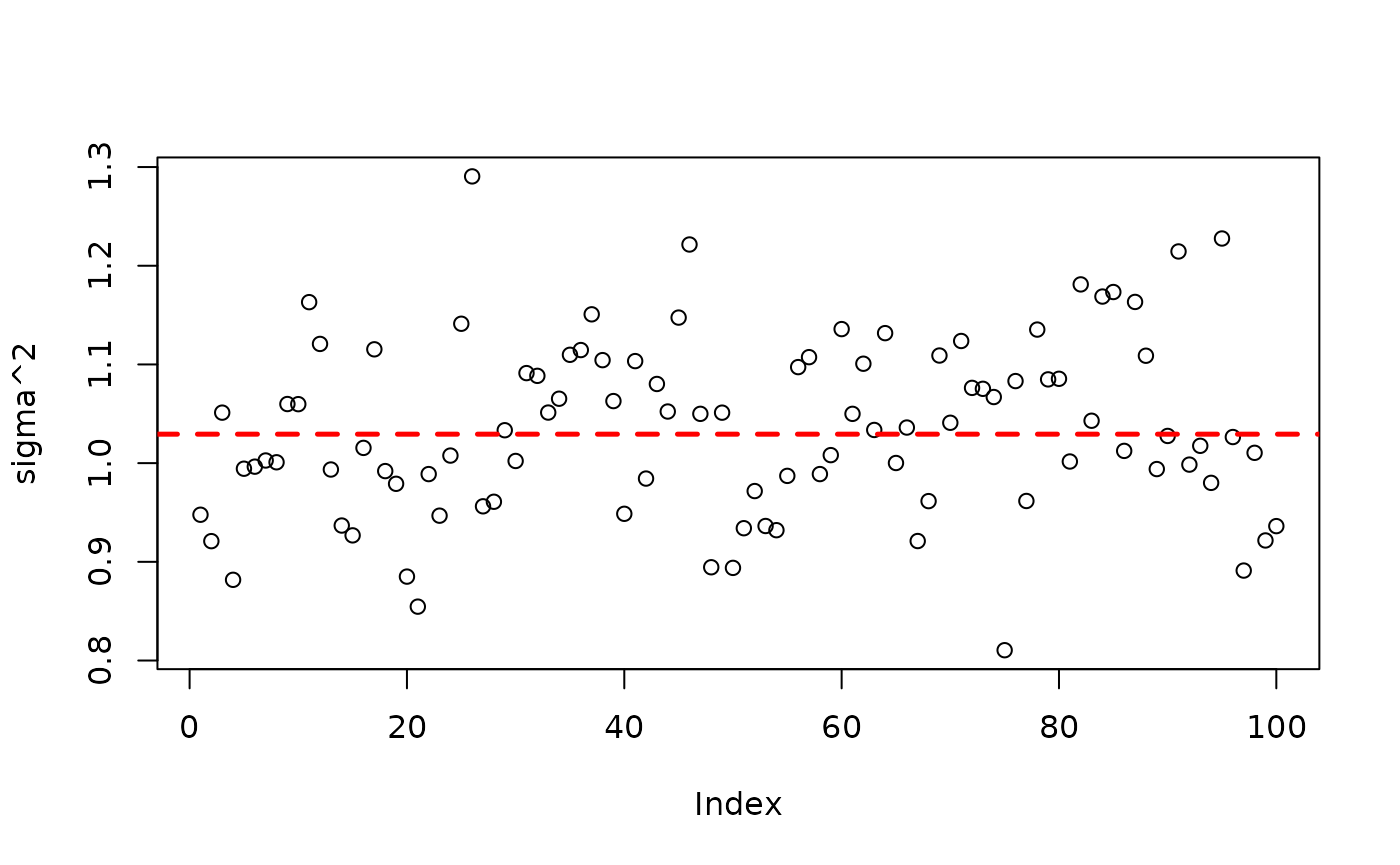
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_warmstart$y_hat_test), y_test,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)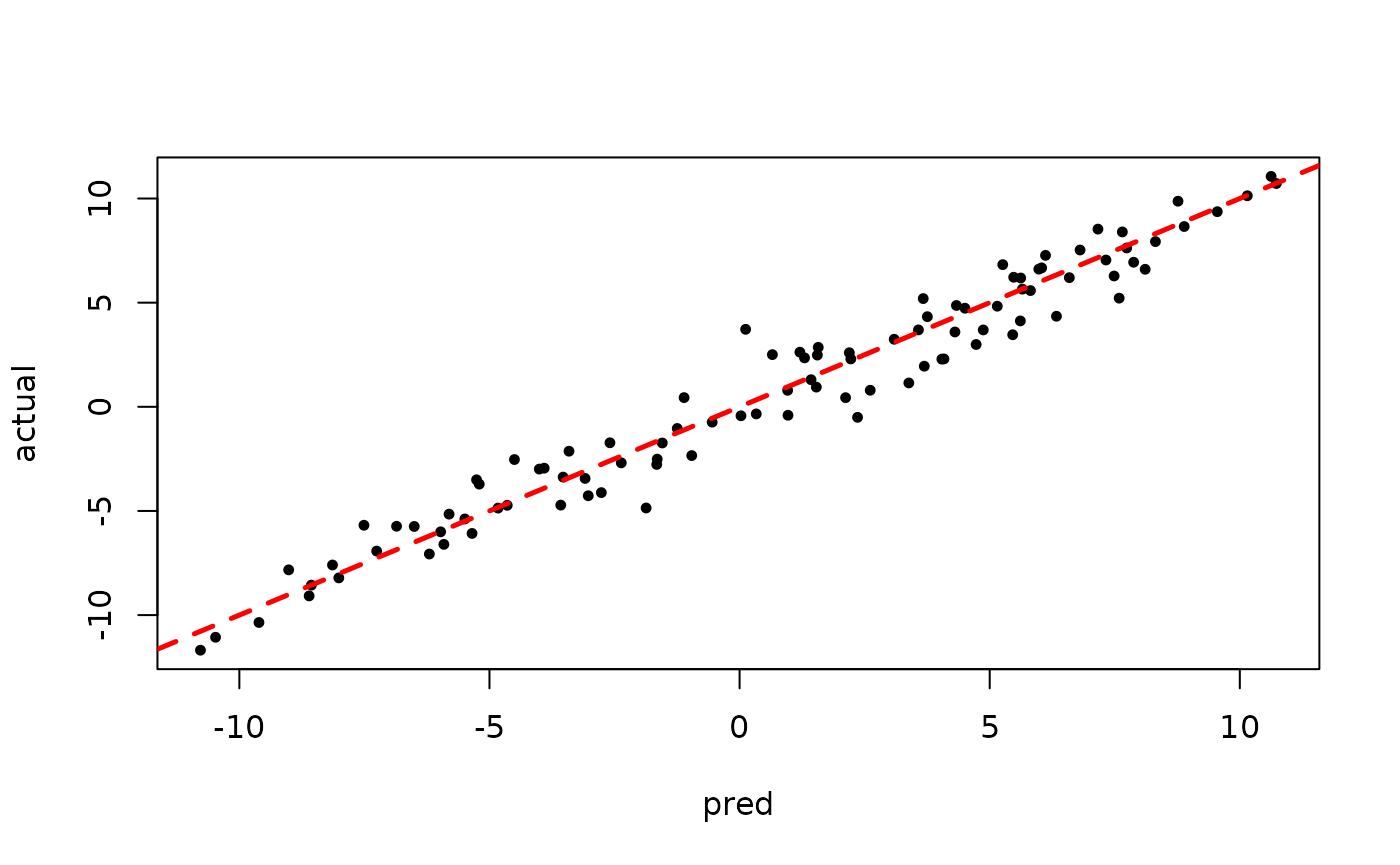
BART MCMC without Warmstart
Next, we sample from this ensemble model without any warm-start initialization.
num_gfr <- 0
num_burnin <- 100
num_mcmc <- 100
num_samples <- num_gfr + num_burnin + num_mcmc
bart_params <- list(sample_sigma_global = T, sample_sigma_leaf = T, num_trees_mean = 100)
bart_model_root <- stochtree::bart(
X_train = X_train, W_train = W_train, y_train = y_train, group_ids_train = group_ids_train,
rfx_basis_train = rfx_basis_train, X_test = X_test, W_test = W_test, group_ids_test = group_ids_test,
rfx_basis_test = rfx_basis_test, num_gfr = num_gfr, num_burnin = num_burnin, num_mcmc = num_mcmc,
params = bart_params
)Inspect the MCMC samples
plot(bart_model_root$sigma2_global_samples, ylab="sigma^2")
abline(h=noise_sd^2,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)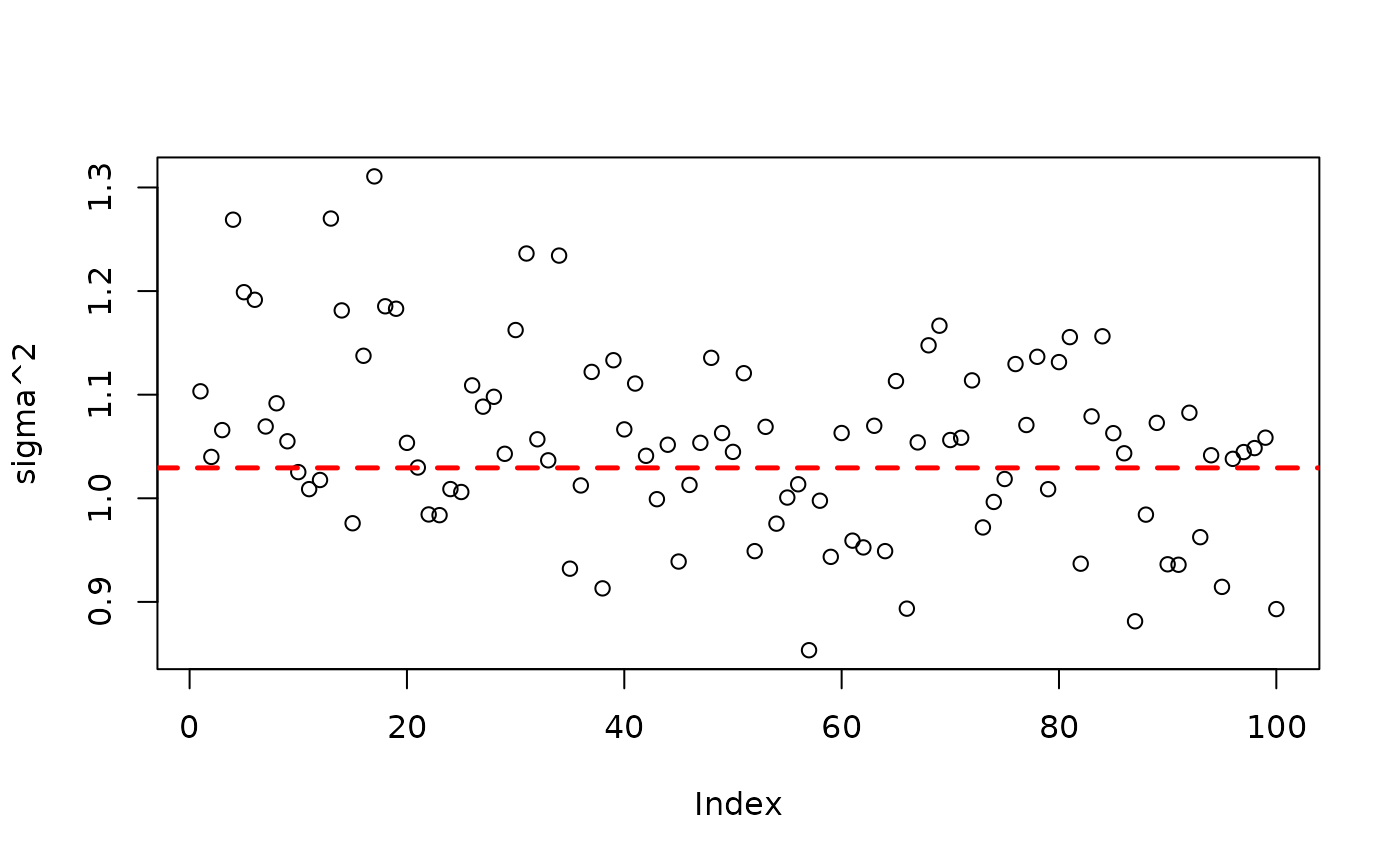
plot(rowMeans(bart_model_root$y_hat_test), y_test,
pch=16, cex=0.75, xlab = "pred", ylab = "actual")
abline(0,1,col="red",lty=2,lwd=2.5)